Magnesium alloys and aluminum alloys are two commonly used metal alloy materials, each with their own set of characteristics and applications. Here are some key differences between the two:
1.Density:
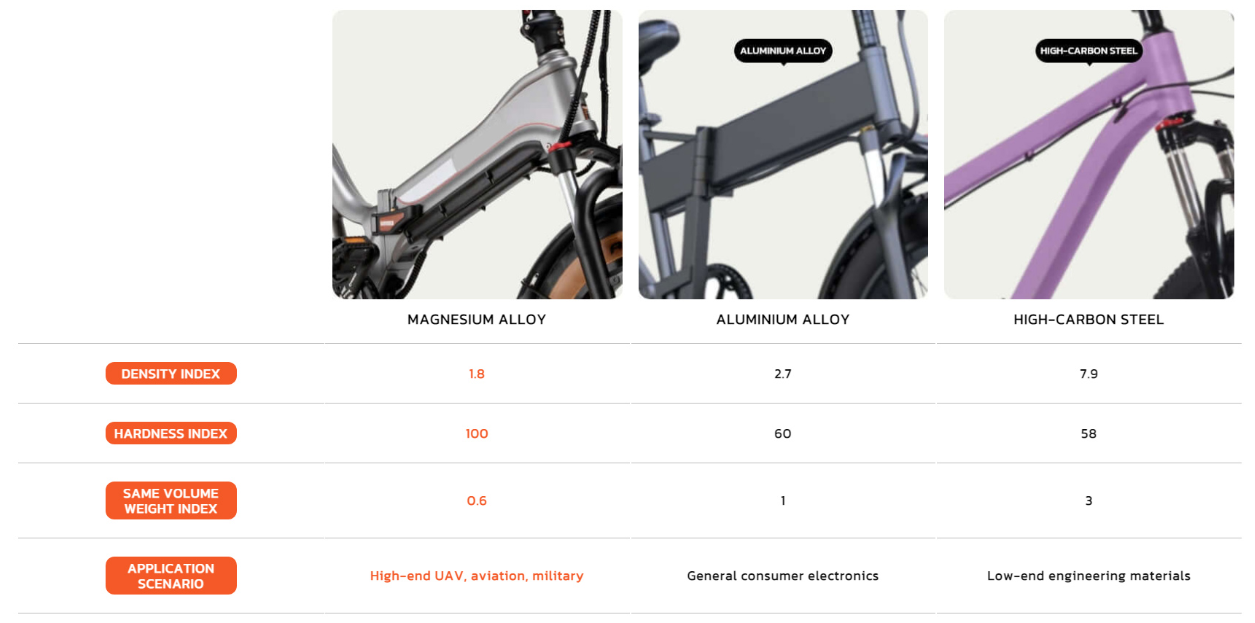
Magnesium alloys have a density of approximately 1.7-1.9 g/cm³, making them one of the lightest structural metals available.
Aluminum alloys have a slightly higher density, around 2.7 g/cm³.
2.Strength and Hardness:
Generally, pure magnesium is relatively low in strength, but its strength can be increased through alloying. However, magnesium alloys typically have lower strength compared to aluminum alloys.
Aluminum alloys usually exhibit higher strength and hardness, especially high-strength aluminum alloys that have been heat-treated.
3.Melting Point:
Magnesium alloys have a lower melting point, generally around 650°C.
Aluminum alloys have a higher melting point, generally between 660°C to 760°C.
4.Corrosion Resistance:
Magnesium alloys are more prone to corrosion without protection, especially in moist or saline environments.
Aluminum alloys possess better corrosion resistance, especially when an oxide layer is formed or after surface treatment.
5.Machinability:
Magnesium alloys, due to their lower melting point and hardness, have better machinability during processing.
Aluminum alloys are also easy to machine, but the machining parameters may need to be adjusted based on the specific type of alloy and its heat treatment state.
6.Thermal and Electrical Conductivity:
Aluminum alloys have better thermal and electrical conductivity than magnesium alloys, making them more common in applications requiring good heat dissipation or electrical conduction.
7.Applications:
Magnesium alloys are typically used in applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as parts in aerospace and automotive industries, and casings for portable electronic devices.
Aluminum alloys have a broader range of applications, from structural components in construction to parts in automobiles and aircraft, as well as household appliances and electronic products.
8.Cost:
The cost of magnesium alloys is generally higher than that of aluminum alloys, partly due to the higher extraction and processing costs of magnesium.
9.Recyclability:
Both magnesium and aluminum alloys are recyclable, but the recycling chain for aluminum alloys is more mature and has a higher rate of recycling.
Understanding these basic differences can help engineers and designers choose the most suitable material for their specific applications.